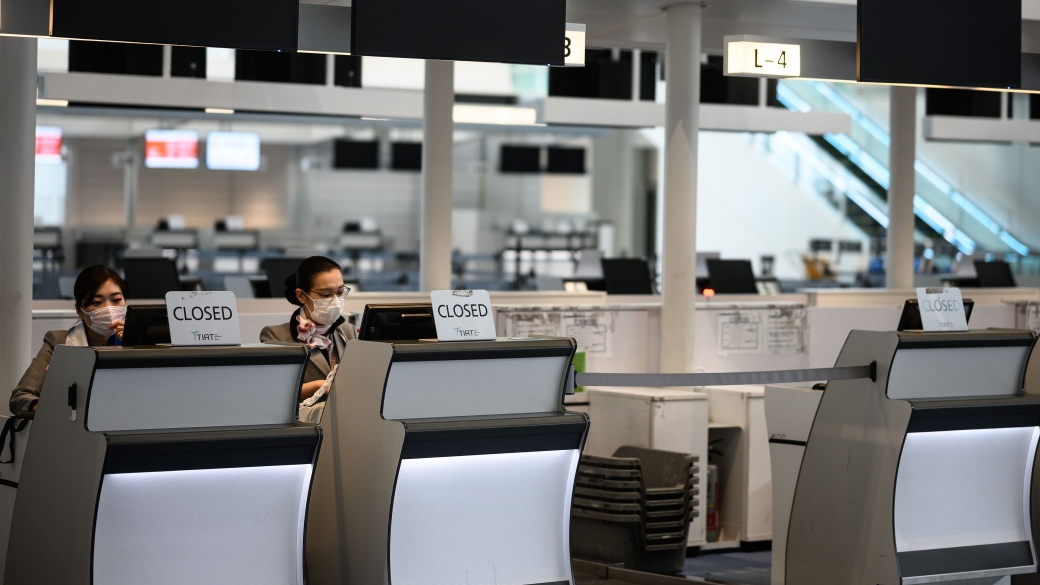
Confirmed cases of the novel coronavirus (COVID-19), which first appeared in China at the end of last year, now exceed 115,000 as of March 10 and are likely to climb significantly higher. While over two-thirds of the total confirmed cases are in mainland China, the vast majority of new cases reported since February 25 have occurred outside the country. What was initially seen as a largely China-centric shock is now understood to be a global crisis. The virus’s spread has regrettably borne out analysts’ downside scenarios, with investors digesting the implications of disrupted supply chains, official containment measures, and spillovers from the real economy to financial markets. A decision by two of the world’s largest energy producers to maintain current levels of production, despite falling energy prices, has further unnerved investors while questions about governments’ abilities to mount an effective and coordinated response linger. The increased uncertainty has led to financial market volatility last seen during the global financial crisis.
Follow us on Instagram @Coronaviruslegal
© Coronavirus Legal 2020. All Rights Reserved